How Deep is Google’s Love?: Where the In-Depth Articles have Gone (and What it Means for You)
Recently, Google appears to have made a significant change to its search results page that eliminated several in-depth articles for many clients. We’ve taken a deeper dive into this development to see what it could mean for brands and high-profile individuals, and the PR professionals who work with them.
As you know, when searching for a brand or an individual, the Google search results page presents a variety of relevant content pieces and types of media to satisfy the query. Often this means a company’s own webpage will appear at the top, followed by third-party content such as Wikipedia and news sources. There may also be social media results (if an individual or brand actively maintains these platforms), along with image results or video content.
Several years ago, Google introduced a section within top search results they called “in-depth articles”. These results looked very similar to other search results, but came from longform media outlets like Variety, Rolling Stone, or The New York Times Magazine. Often, they were a seminal article about the brand in question – articles that may have been placed by their PR teams.
Including these articles on the top results page seems to have been Google’s way of ensuring that a greater variety (and deeper) content would appear in this prime spot. Their inclusion, and the actual articles that appeared within that section, were governed by a different set of algorithms than most search results.
Recently, this section disappeared from all search pages for brands and executives. This happened without any announcement or acknowledgment on the part of Google. It is important to note that in-depth articles for many brands and individuals contained negative content. At the same time, it was the place where particularly engaging longform journalism made its way onto the prime real estate of Google page 1 for a brand.
The ramifications of Google’s elimination of this section are yet to be seen, and their motivation can only be assumed to be “less intervention” following high profile criticism of potential bias in their algorithms.
A whole host of interesting questions arise from Google’s move: What is the corporate (and civic) responsibility of those who hold the world’s data in their hands? Are there cases for intervention? Who decides what those are?
It is interesting to note that alongside this mysterious disappearance, a recent Five Blocks study of CEO search results found there are far fewer news sites (sites such as CNN, CNBC, and others) on the first couple of pages of searches for a CEO compared to a year ago. In addition, those pages feature many more profile sites, where one would find more dry facts (often created by the brand), and less news.
This marked difference in the presence of news within the organic results over the course of the past year, alongside the recent removal of the in-depth article section, means that page 1 of search for brands and individuals will contain far more“owned” content – i.e.: information they control.
For some brands this would appear to be a positive turn of events, but for many this trend means they will not automatically have great media pieces (which they often earned by being genuinely great) appear prominently in searches. It means they will need to work harder to deliberately ensure that the best third-party media does in fact place highly within their profile. Savvy communications teams will find ways to enhance their brands’ online presence within these brave new parameters.
— Sam Michelson, with Sara K. Eisen
Learn about Digital Reputation During a Crisis at the 2019 PR News Crisis Management Summit in Miami Beach – Thursday, February 28th
When crisis strikes, a company’s digital reputation becomes stressed and vital to their health. Five Blocks President, Howard Opinsky, will offer his insights at the Summit on the impact that crises have on digital reputations and what brands and individuals can do to prepare to weather the storm. Our team of digital reputation experts will also be on-hand to discuss how you can take control of your internet search results and shape them to best reflect your real profile. Join us at the Summit on February 27-28 in Miami Beach and don’t miss Howard and fellow panelists as they recount some of the best handled B2B crises and best practices in crisis preparedness at two sessions on Thursday, February 28. Learn more about the PR News Crisis Management Summit here.
Digital Reputation Management: It’s Not All About Burying Results

I posted the following on Business Insider in response to a post that focused on the underbelly of the Digital Reputation Management industry.
Many companies and individuals who have online reputation issues are not trying to bury negative reviews or articles. Instead, they are working to make sure that people searching for them online find what they are looking for. This need often arises when the brand or individual has not made any effort to create an online presence (think either a minimal website or none at all, no participation in social media, no business profiles, no YouTube channel, etc.)
Take for example a financial services firm which mostly arranges M&A’s. An article on a popular business news website portrays a potential upcoming deal for the company in a negative light – probably due to the author’s view of the industry in which the company is involved. The financial services company isn’t active online. They have a one-page website that does not appear prominently in searches online. Most of the prominent mentions of the firm seen in a Google search contain contact information, SEC documents and occasional mentions on investor portals.
The goal of an online or digital reputation management program for this client (and many like it) is to help the client present their brand appropriately online. There really is no need to subvert any search engine algorithm or bury any results.
The Digital Reputation Management program would consist of elements such as:
- Building out the current website so that it is technically sounds and contains content that will help it rank well in search engines.
- Creating company and individual profiles on sites like: LinkedIn, CrunchBase, and others.
- Working with Wikipedia editors to correct any incorrect information appearing in Wikipedia – including providing sources to editors that they can quote.
- Registering the brand and key individuals on social media websites that may be appropriate to use in the future (Twitter, Google+, etc.).
- Working with the client’s communications team (or their external PR firm) on opportunities for publishing thought leadership materials in one or more relevant media outlets.
In short, there are many tools at the disposal of digital band management professionals that, rather than being exercises in removing negativity, are proper digital branding and communication efforts. Rather than focusing on fooling the algorithm (in the long term Google will beat you!), serious companies should be considering digital reputation management strategies and tactics that take advantage of Google’s algorithm and its ability to detect relevant, authoritative content from a variety of sources.
So, You’re Working on Digital Brand Alignment for a COUNTRY!
We have had opportunities to work with governments, NGO’s and organizations of all types.
Before we can advise a client on the steps they should be taking, we need to understand the context. When working with a country, it is important to ascertain what results are normal for a country.
Clients will usually say something like, “CIA Fact Book?! Why is the entry for CIA Fact Book coming up so high for us? Does Google consider our (banana?) republic a terrorist state?”
To answer these and other questions we start by looking at the expected results for countries.
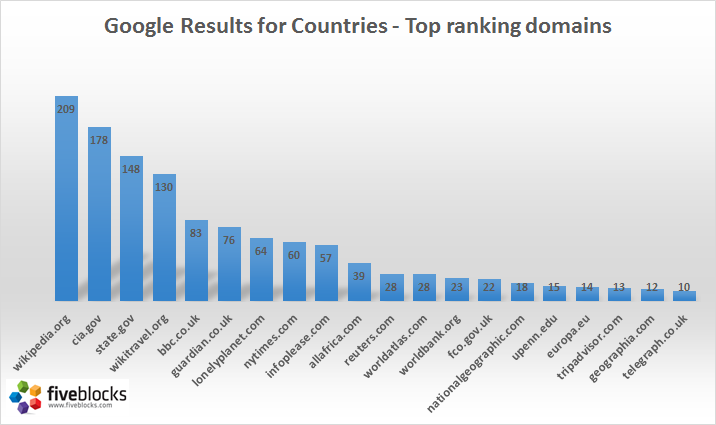
Below is a chart for Dec 17, 2012 showing the most frequently appearing domains for countries searched in Google. This table considers the first page of Google as seen in the US only. Note that results in any specific location may vary, so that searching in Google.fr (France) would be expected to yield more sites that pertain to that location.
Numbers on the chart indicate the number of countries displaying this domain in their first page Google results.
It is interesting to note that cia.gov and state.gov dominate the results along with the ubiquitous Wikipedia. If you are responsible for the branding of a country, this table serves as some initial context. Any site here that also appears for your country should not be a shock.
One of the surprises for me was a site called infoplease.com (by Pearson Education) which ranks for 57 countries* even though it is of lower quality! I’m actually not sure what to make of it – it may well appear in situations where a country has not done even a basic job of creating or curating web content that can outrank this low quality scraper search site. (*In case you want to dig deeper, the complete list is at the bottom of this post.)
Also – the role of community-generated content for country results should not be underestimated – Wikipedia and Wikitravel each serve as top domain results for most countries. This certainly suggests that ignoring community content would be unwise.
So what’s your strategy?
In general, your goal should be to design the ultimate branding and focus. Perhaps you would prefer results focused more on industry rather than tourism or political news? With that in hand, you’ll develop strategies to achieve these goals.
If you have questions or comments or would like to dig deeper into the data with us – feel free to drop us a line.
*Countries for which infoplease.com ranks in the top page of Google results:
1. Algeria
2. Andorra
3. Angola
4. Argentina
5. Armenia
6. Bahamas
7. Bangladesh
8. Bosnia and Herzegovina
9. Burundi
10. Cambodia
11. Cameroon
12. Cape Verde
13. Chile
14. Colombia
15. Cuba
16. Denmark
17. El Salvador
18. Equatorial Guinea
19. Ethiopia
20. France
21. Gabon
22. Guatemala
23. Guyana
24. Haiti
25. Honduras
26. Hungary
27. Indonesia
28. Italy
29. Kyrgyzstan
30. Laos
31. Lithuania
32. Malawi
33. Malaysia
34. Mali
35. Marshall Islands
36. Micronesia
37. Monaco
38. Mongolia
39. Morocco
40. The Netherlands
41. Nicaragua
42. Nigeria
43. Papua New Guinea
44. Peru
45. Poland
46. Portugal
47. Romania
48. São Tomé and Príncipe
49. Senegal
50. Spain
51. Uganda
52. Ukraine
53. United Kingdom
54. Uruguay
55. Uzbekistan
56. Venezuela
57. Yemen
Domino’s Pizza Retrospective: Why PR Must Own the “Google Top Ten” in Today’s Era of Online Reputation Management
This piece was written by David Goldman and originally appeared in the Daily Dog on April 27, 2009.

PR firms are responsible for their client or company’s reputations. Similar to the Domino’s fiasco, if a negative video or blog reaches into the top ten of Google search results for a client’s brand name, it’s called a “PR problem.” So why aren’t PR firms called on more often to fix the problem with their client’s online reputation?
One answer is that most people assume that Google search results are like the weather. We have the tools to measure them and possibly predict them, but we can’t change them. Fortunately, the situation isn’t that bad. Experienced online reputation management (ORM) firms working in tandem with PR firms can control a client’s search profile. The best way to get rid of negative results on Google is to take control of your reputation online. Another answer is that online reputation management should belong to the client’s SEO firm. This is a missed opportunity for PR and oftentimes untrue.
Progressive agencies are taking ORM seriously, partnering with firms or making internal hires to accommodate the growing need for bridging their traditional and even online efforts to ORM services. They realize that PR firms are competing with SEO companies to provide these services and understand the strategic as well as the financial sense in getting there first. Agencies should understand that they are often creating the message and image of the brand while SEO firms are technology people.
The Domino’s Case Study—Timely ORM Tips to Consider
Just over a week after the Domino’s “PR Nightmare,” many communications professionals are asking two questions: What can the brand do to salvage its reputation after the fact? And what can we do to prevent our clients from a similar crisis? Here is how our firm would work with Domino’s PR to clean up the mess:
There are at least three things that Domino’s Pizza should be doing now to clean up their online reputation. Although the buzz around the infamous video will continue to wane, the postings and marketing articles about the incident have the potential to linger for months, possibly years, unless the brand takes action. If you’re Domino’s, here’s what you need to do today:
1. Tweet to a stronger presence online. A company that is such an important part of American culture should be actively creating positive buzz online. Domino’s didn’t even have a Twitter account until after the crisis broke.
Pizza Hut recently posted a job offer for a summer intern to work on their Twitter account (see the posting here: http://news.cnet.com/8301-17852_3-10223100-71.html). That’s the type of planning that helps soften a social media crisis when it arises. With 125,000 employees at their disposal, Domino’s could easily distribute an internal memo advocating that employees open Twitter accounts and post positive comments about the work environment and the company. Twitter is one of the fastest ways to have a positive impact on a brand. Domino’s employees have a real interest in making their brand popular and keeping it strong. This will not only help supplant the negative content from the top search results in time, but help prevent a future crisis as well.
2. Develop and execute a video strategy. Currently, most of the videos that appear on YouTube and video-sharing websites for the keyword “dominos” are not about Domino’s Pizza. Had Domino’s occupied the top ten spots on YouTube for the keyword “dominos,” the effects of a rogue negative video would have been greatly mitigated. There was a lost opportunity as the millions of searchers for the keyword “dominos” could have also been exposed to positive messages from the brand in the form of videos.
In addition, the brand’s TV commercials should be systematically re-posted and optimized so they occupy the top spots for video searches of the word “dominos.” Management should also ask employees to create YouTube videos promoting the brand, empowering the employees to feel like they are part of the solution, not only the problem.
3. Go “deep”—leverage mini-sites. Domino’s probably thought that by having a consumer-focused website and a corporate homepage they had their bases covered. In truth, their web presence is shallow.
Creating mini-sites on a few important topics can garner excellent PR while protecting the brand’s online reputation. Some topics Domino’s could consider for mini-sites: a) Passion for Pizza (The Internet is the perfect medium for expressing the passion you have for your product or service.), b) Domino’s and the Environment (focusing on recycling or other green initiatives), and c) Domino’s Scholarships (or Domino’s Community Projects). Each of these mini-sites can occupy a top spot in the Google results if created and optimized by ORM experts.
The Bigger Picture—Why PR Must Own ORM
All of these suggestions are facets of a full-service online reputation management program. When ideas like these are implemented together with a program of reputation management focused on positive articles and links, a negative situation can be transformed into a reputation-building opportunity.
Although Online Reputation Management (ORM) has existed for several years, today the need for this service is more relevant than ever. It isn’t a question of whether companies need and seek this type of service anymore. The real question is: To whom will they turn?
We have met with many PR firms in the U.S. who offer a “blogging strategy,” creating and maintaining an optimized corporate blog for their clients. While this is an excellent first step, online reputation management requires much more than one well-run blog. These firms often subscribe to outside services in order to track their client’s reputation online, but rarely do they offer a solid measurable solution.
So what is the better model?
Answer: Stop offering blogs and start offering “search profile optimization.” A search profile is essentially what someone sees when they search for your client’s brand or product name; it’s the “Holy Grail of Search;” it’s the Google top ten. Today, there are several ORM firms with whom agencies and consultants can partner—offering a white-label solution to their clients to improve their search profiles. The ORM firm provides charts and graphs that track the progress of their work for the PR firm to merchandise back to the client with their ‘look and feel.’
There are methods (especially for clients who are vulnerable to the “Domino’s Effect”) that can greatly reduce the collateral damage of a scandal before it takes place. By “owning” the Google top ten before a crisis breaks out, PR firms can effectively prevent a catastrophe. On a brand’s marketing team, only the PR firm knows when the bad news is coming. Whether it’s layoffs, a poor earnings report or a discrimination lawsuit, this knowledge can be used to minimize damage to the brand by securing the Google top ten in advance of the negative announcement.
Providing ORM services for clients is a way for PR firms and crisis communications professionals to stay vital to their clients and gives clients another reason to stick with their agencies. In this uncertain economy, every PR professional should be finding new ways to increase revenues and retain their clients. Offering ORM services allows PR firms to do both.